SharePoint is one of the most widely used enterprise collaboration platforms in Microsoft 365. It empowers teams to share files, collaborate in real-time, and streamline business workflows. But without the right controls, your SharePoint environment can become a risk vector for data leaks and threats.
This guide breaks down essential SharePoint Online security best practices that help organizations safeguard content, meet compliance standards, and reduce vulnerabilities—without slowing down business productivity.
Why Microsoft SharePoint Security Is Critical
SharePoint often houses:
- Corporate documents
- Financial records
- Client information
- Intellectual property
A misconfigured site, overly permissive sharing link, or weak access controls can expose sensitive data internally or to unauthorized external users.
Security isn’t just about permissions—it’s also about classification, monitoring, governance, and user behavior.
SharePoint Security Best Practices
SharePoint Security Best Practices Checklist

Below, we explore Microsoft 365 SharePoint Online best practices in detail to help organizations secure data, manage access, and enable safe collaboration.
1. Configure Secure External Sharing Settings
Sharing is at the heart of collaboration—but external sharing must be controlled.
Best practice:
- Disable or limit “Anyone” sharing links by default
- Restrict external sharing to specific domains or authenticated guests only
- Set expiration for all external links
Tenant-level External Sharing Settings in the Microsoft SharePoint Admin Center:
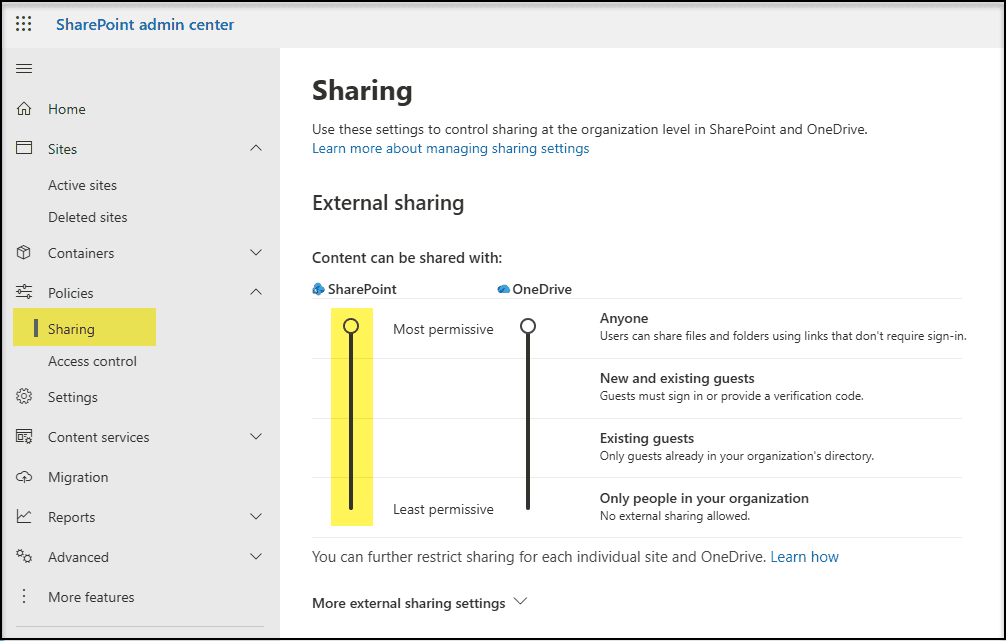
Site-level settings with more restrictive policies
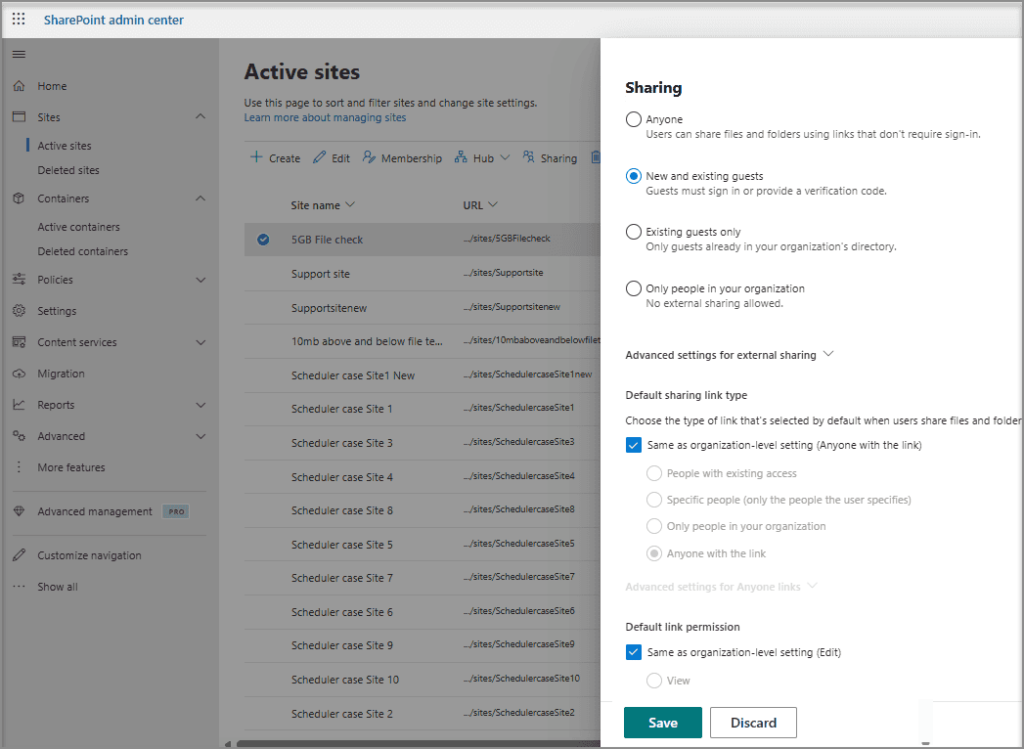
2. Use Principle of Least Privilege with Permissions
Give users only the access they need:
- Use default SharePoint groups (Owners, Members, Visitors)
- Avoid granting individual permissions directly
- Use Microsoft 365 / Entra ID groups where possible
This reduces risks from insider threats and accidental data exposure.
3. Apply Sensitivity Labels and Classification
Microsoft Purview Sensitivity Labels help classify and protect content based on data sensitivity- public, internal, confidential, or highly confidential.
Sensitivity label options in the admin portal

With sensitivity labels you can:
- Enforce encryption
- Restrict sharing
- Apply data loss prevention (DLP) rules
- Extend permissions even on downloaded copies
This helps enforce consistent data protection across SharePoint, Teams, and OneDrive.
4. Protect Accounts with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Passwords alone aren’t enough—enable MFA for all users, especially administrators and privileged roles.
MFA dramatically improves security and defends against credential-based attacks like phishing and brute force attempts.
5. Implement Conditional Access Policies
Use Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD) Conditional Access to control how, when, and where SharePoint data can be accessed:
- Require compliant or managed devices
- Restrict access from untrusted locations
- Require MFA for sensitive sites
This adds an adaptive layer of protection based on risk context.
6. Enforce Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP policies help detect and block:
- Sharing of sensitive information (PII, PCI, health data)
- Unintentional data exfiltration
- Content shared with unauthorized users
DLP integrates with SharePoint to monitor and protect data stored in document libraries and sites.
Learn More Here: Microsoft Learn: About DLP
7. Monitor and Audit Activity
Turn on SharePoint Audit Logs using the Unified Audit Log in Microsoft Purview.
Visibility into user actions is key to SharePoint security.
Track access, sharing, deletions, and permission changes Set alerts for Suspicious behavior.
Monitor external user access and sharing activity to support SharePoint external users audit.
8. Secure Admin Accounts & Roles
Admin privileges should be:
- Assigned only when necessary
- Covered with strong authentication policies (MFA, Conditional Access)
- Managed with Privileged Identity Management (PIM)
Minimizing admin accounts reduces the attack surface for targeted threats.
9. SharePoint Site Ownership Best Practices
SharePoint site owners control permissions and sharing, making them critical to security.
Best practices:
- Assign at least two site owners per site
- Choose trained, internal users as owners
- Limit Full Control to owners only
- Review ownership regularly to avoid orphaned sites
- Protect owners with MFA and Conditional Access
Strong ownership governance reduces risks and protects SharePoint Online data.
10. Educate Your Users
People are both your biggest asset and biggest risk.
Train employees to:
- Recognize phishing and social engineering
- Understand how to share securely
- Use sensitivity labels appropriately
- Report potential threats immediately
A trained workforce helps prevent simple mistakes from becoming security incidents.
Common Microsoft SharePoint Security Pitfalls
❌ Leaving external sharing open to “Anyone”
❌ Granting full control to too many users
❌ Failing to monitor activity logs regularly
❌ Not enabling MFA on critical accounts
❌ Assuming classification or DLP is “set and forget”
Final Thoughts
Securing SharePoint is not a one-time task—it’s an ongoing commitment involving people, process, and technology. By following these Microsoft SharePoint security best practices and maintaining vigilant governance, your organization can enjoy secure collaboration without compromise.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes—when properly configured, SharePoint Online’s robust security built into Microsoft 365 can protect sensitive data with encryption, classification, and access controls.
Use restrictive tenant and site sharing settings, require authentication, set link expirations, and combine this with DLP rules to block sensitive content from being shared externally.
Yes—sensitivity labels can persist even on downloaded documents, enforce encryption, and prevent unauthorized access if content leaves the SharePoint boundary. Refer Microsoft Learn: Sensitivity Labels for more details.
Yes. SharePoint has audit logs in Microsoft 365 Compliance Center, where you can track activities like file access, edits, deletions, and permissions changes.
Note: To begin, auditing must be enabled in the Site Settings to ensure that activity data is collected.
At minimum quarterly, or whenever major changes occur (such as onboarding new teams, restructuring sites, or external collaboration changes).
Use Microsoft Purview audit logs to monitor external users’ access, sharing activity, downloads, and permission changes across SharePoint sites.

















 Migrate
Migrate
 Manage
Manage











 Migrate
Migrate
 Manage
Manage